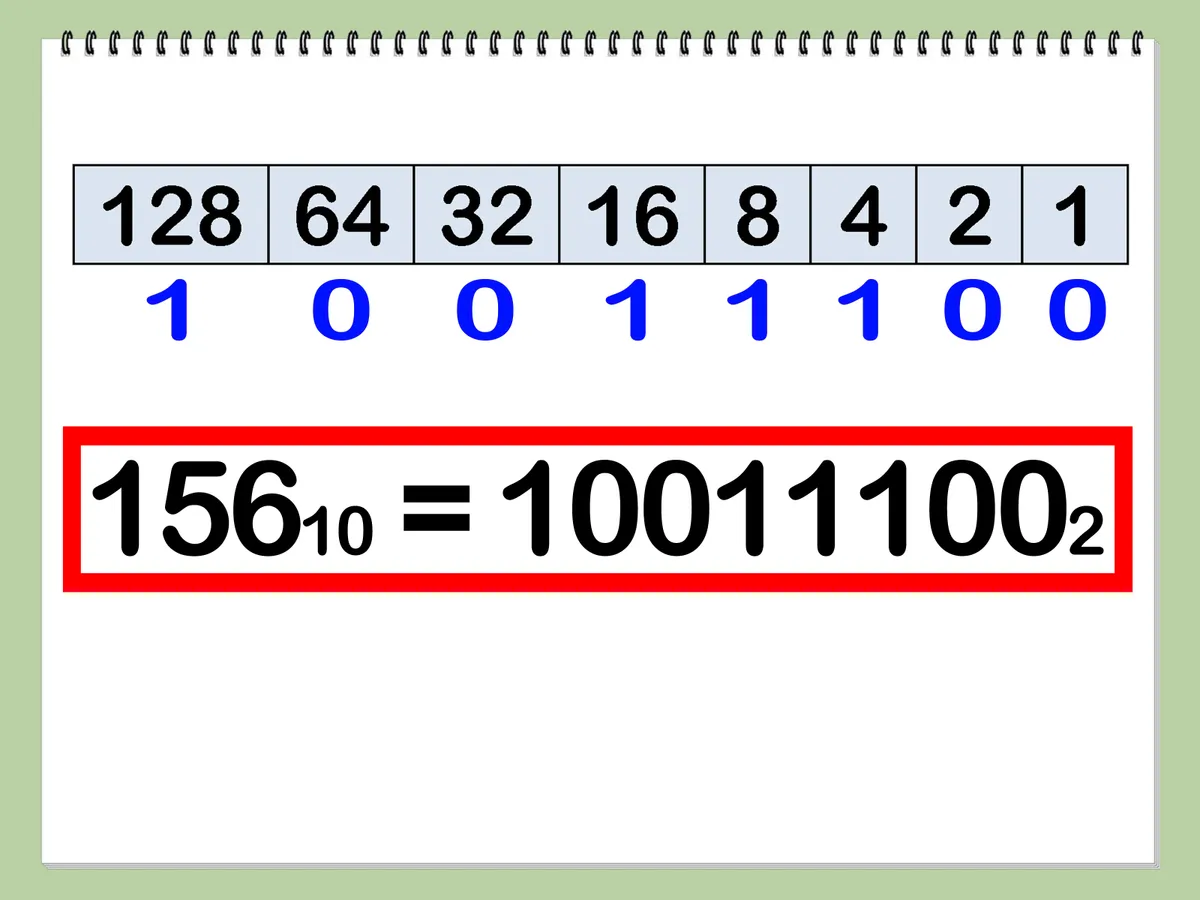
Binary
A signal needs to differentiate one value from another. These are represented by the 0's and 1's. These are used in things such as true and false statements where 1 is true and 0 is false, electronic signals set with HIGH (voltage present) LOW (voltage not present)
CPUs discern 0's and 1's through voltages, set a defined voltage range to be 0 and 1 to make up for noise
Max number of a binary number is 255 (Just like colour profiles)
Hexadecimal
A base 16 method allowing computers to more easily display data to humans. Contain the numbers from 0-9 and A-F.
These are used in things like memory addresses, encrypted or compressed data, integers, floating points, and text
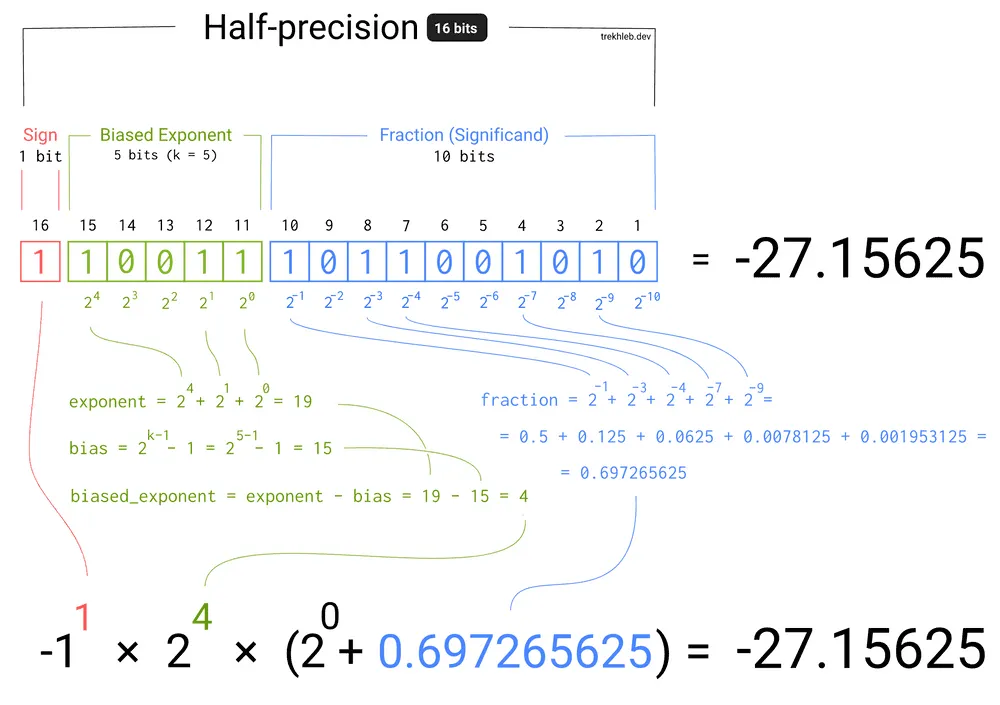
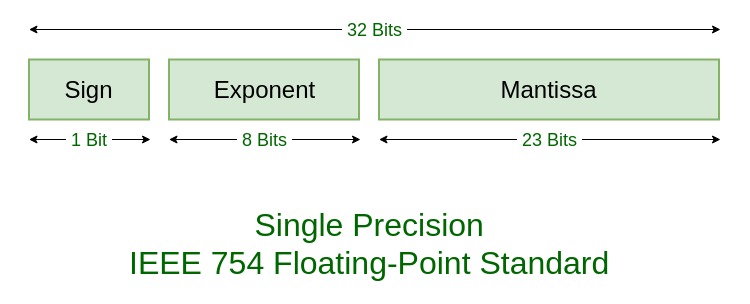
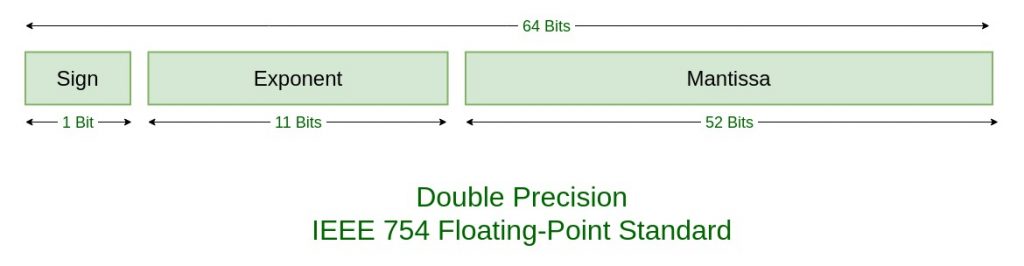
Representing Fractional Numbers
Decimal has been extended to include negative powers of 10
Scientific notation is often used to show this
Mantissa of the binary number is the actual number, and the start is where you place the decimal
ASCII
Each letter, digit, punctuation is represented by an 8-bit number
Advantages: Uppercase letters are contiguous, Lowercase letters are contiguous, Digits are contiguous
Disadvantages: Really only English is supported
Unicode
Supports most writing systems, math symbols, emojis
It can store these characters in UTF-8 or UTF-16
UTF-8 stores unicode characters using 8-32 characters. English (8-bit) and latin (16-bit) are prioritized
UTF-16 stores unicode characters using 16-32 characters